Reprocessing strategy in event-driven integrations
Reprocessing is crucial to maintain the stability of integrations. This article explains how reprocessing failed records can:
Prevent data loss.
Reduce manual intervention.
Keep systems running smoothly.
Understanding the value of a reprocessing pipeline helps you see how it supports efficient and reliable integration processes.
Reprocessing in event-driven architectures
Event-driven architectures (EDA) enable systems to respond dynamically to real-time events by triggering actions based on incoming messages. To manage these events and for better task isolation, integrations can be divided into separate pipelines. For example, a main pipeline can be responsible for reading records, while dedicated pipelines can handle processing, reprocessing failed events, and error handling.
In event-driven integrations, temporary issues like network outages or service unavailability can interrupt message processing. These errors are usually classified as:
Retriable (server-side): Caused by temporary issues.
Non-retriable (client-side): Caused by malformed payloads or incorrect data input.
Without a reprocessing strategy, these errors increase operational overhead, create inefficiencies, and require monitoring to maintain data integrity. A reprocessing pipeline solves this by sending retriable errors back to the processing pipeline.
Reprocessing challenges
Not having a reprocessing mechanism can lead to significant issues when events fail due to retriable errors, resulting in several key challenges:
Data loss: Without a reprocessing strategy, events that fail due to temporary errors such as network issues or system downtime might be discarded, causing critical data loss and inconsistencies.
Manual intervention: Without an automated reprocessing strategy, failed events require constant manual intervention to recover, adding extra workload for IT teams.
Inconsistent states: When events aren't reprocessed, integrations can result in inconsistent states. This happens when systems hold conflicting or incomplete data due to failed events not being retried, leading to discrepancies and the need for manual correction.
These are just some examples that not only affect customer satisfaction but also increase support requests, refunds, and overall business disruptions.
Putting theory into practice
Consider an integration architecture with multiple pipelines, each designed for a specific purpose: one that query records from the database and publishes events, another processes these events individually, a third reprocesses records that failed in the processing pipeline, and a final pipeline manages error handling. In this context, the reprocessing pipeline addresses the challenge of records failing to complete their processes due to temporary, retriable errors, such as network issues or service downtime.
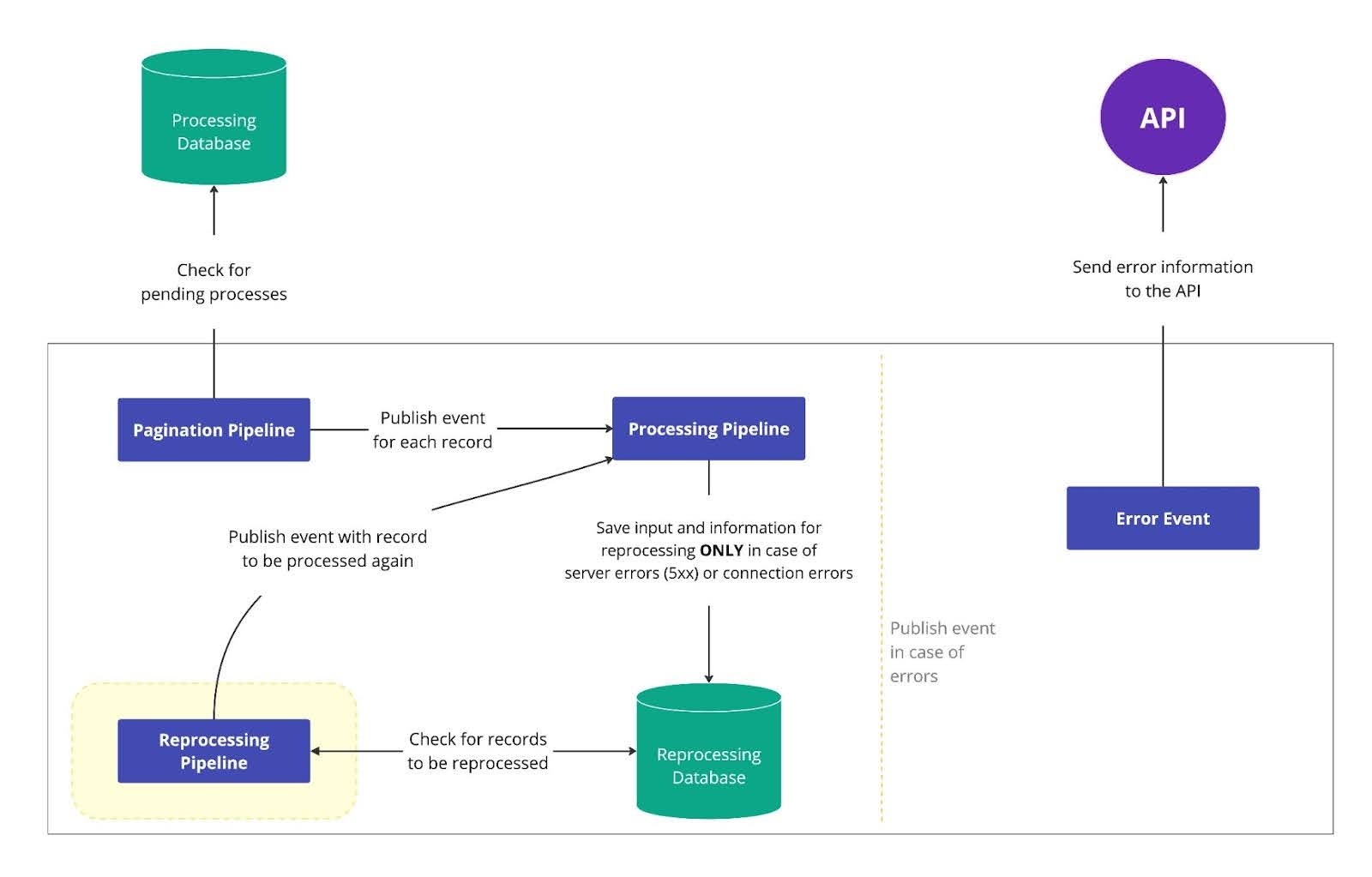
This pipeline provides a solution for reprocessing events that fail to integrate on their first attempt because it automatically retries retriable errors for a set number of attempts.
Consider an integration where purchase orders are sent to a warehouse system. If the warehouse is temporarily unavailable, the processing pipeline saves the failed order with an error status in a control database.
At scheduled intervals, the reprocessing pipeline retrieves these records and sends them back to the processing queue. This ensures orders are reprocessed and sent when the system is available. If an order still fails after the maximum retries, it goes to the error-handling pipeline for further action.
How the proposed solution works
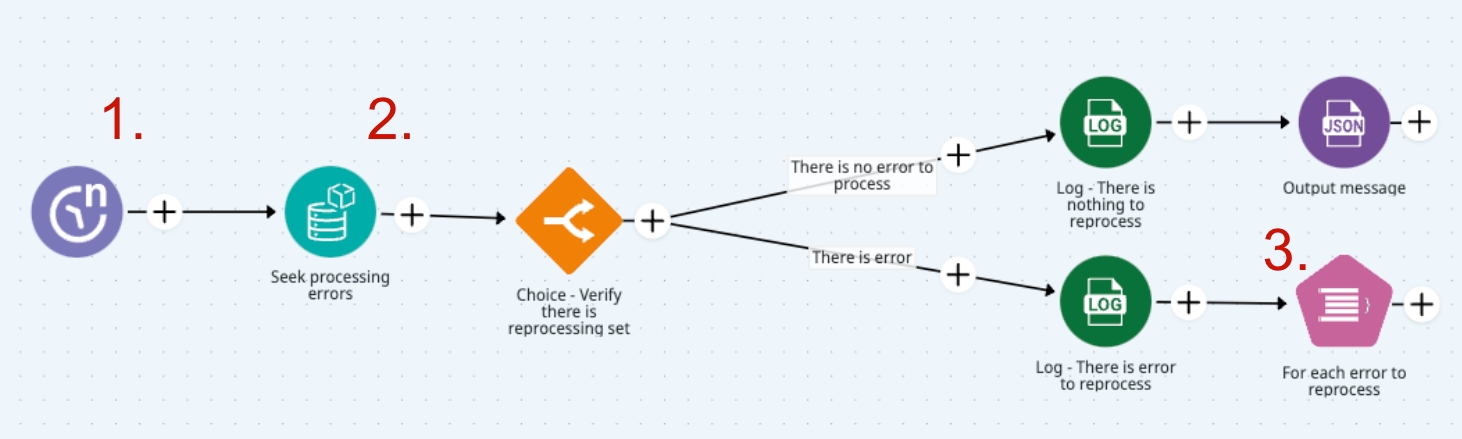
Scheduler Trigger: The reprocessing pipeline starts with a scheduler that triggers the pipeline at regular intervals.
Retrieving failed events: At each interval, the pipeline checks a temporary database for records that couldn’t be processed by the processing pipeline and prepares them for reattempt.
Iterate query records: A loop connector, such as For Each, to iterate through each retrieved record. Within the OnProcess Subflow, the first step is to increment the retry counter to track the number of reprocessing attempts for the record.
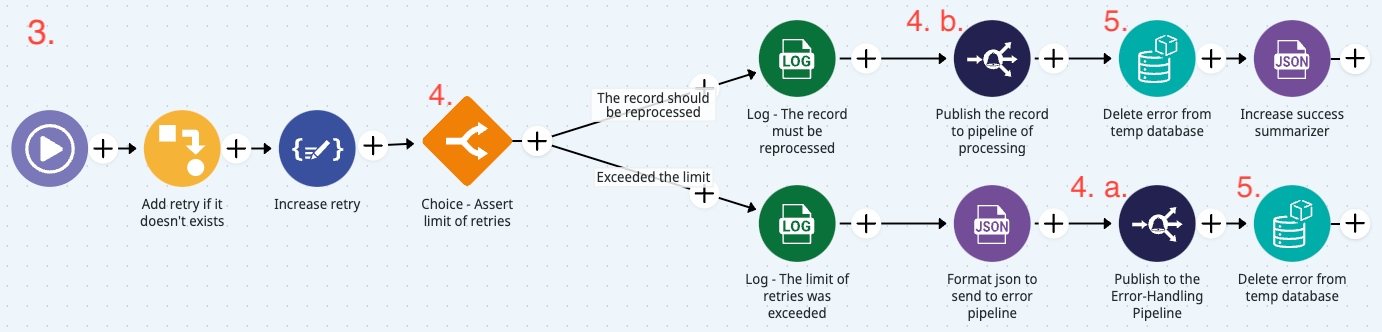
Conditional branching: Based on the retry count and the number of maximum attempts defined, the conditional logic will determine if the record is able to be reprocessed or not:
Record cannot be reprocessed: If a record reaches the maximum retry limit, it’s sent to the error-handling pipeline for further treatment. It’s a good practice to specify the error and notify stakeholders about the maximum retries.
Record can be reprocessed: If a record doesn’t exceed the retry limit, it’s sent back to the processing pipeline for another processing attempt. In this approach, the reprocessing pipeline uses the Event Publisher connector to publish each record back to the processing pipeline.
This approach allows the use of other connectors like the Pipeline Executor as an alternative. This connector supports both asynchronous and synchronous communication, offering more flexibility beyond the Event Publisher.
Record cleanup: After an event is successfully reprocessed or sent to the error-handling pipeline, its record is removed from the temporary database. This cleanup ensures that the database remains efficient and that no outdated data is stored. The process occurs as part of the event lifecycle and ensures that the system is not overwhelmed with old or unnecessary records. Regardless of whether the record is reprocessed or sent for error handling, the cleanup logic ensures that records are not re-read or reprocessed from the database.
Key concepts
Temporary database: A database that temporarily retains failed records until they are reprocessed or reach the configured attempt limit.
Configurable attempts: The number of attempts set based on the reprocessing strategy, allowing multiple reprocessing attempts if necessary. Idempotency is crucial to avoid duplicate processing.
Event Broker: Facilitates communication by routing events from publishers (event publisher connector) to subscribers (event trigger), enabling decoupled and scalable interactions across the system.
Benefits of the reprocessing pipeline
Improved system resilience: The pipeline improves system resilience by reprocessing events that failed due to server-side issues, ensuring that temporary errors are addressed and critical records are preserved.
Reduced manual intervention: By automating the reprocessing of failed events, the pipeline minimizes the need for manual monitoring and intervention after each failure.
Efficient resource usage: With configurable retry limits, the pipeline optimizes resource allocation by aligning retry attempts to business priorities and system capacity, reducing the risk of overloading resources.
Seamless integration with error handling: Once the retry limit is reached, the pipeline sends the event to an error-handling pipeline, ensuring that unresolved events are managed without interrupting the overall system flow.
Final thoughts
In an event-driven architecture, temporary errors are inevitable. However the reprocessing pipeline ensures that records that failed due to server-side errors can be reprocessed without disrupting the integration. By managing these records, the pipeline efficiently handles critical data and maintains the continuous operation of event-driven integrations.
For more information about the reprocessing pipeline, event-driven architectures, and strategies for scalable integrations, explore our Documentation Portal, visit Digibee Academy for courses, or check out our Blog to discover more resources and insights.
If you have feedback on this Use Case in Action or suggestions for future articles, we’d love to hear from you. Share your thoughts through our feedback form.
Last updated
Was this helpful?