Object Store
Discover more about the Object Store connector and how to use it on the Digibee Integration Platform.
Object Store makes operations to store any document in the Object Store of Digibee. It's a simple and quick way to save useful JSON-type information, which has operations to help in multiple uses during the creation of a pipeline.
Parameters
Take a look at the configuration parameters of the connector. Parameters supported by Double Braces expressions are marked with (DB).
Account
Account to be used by the connector. This item can't be changed.
Digibee Object Store Account
String
Operation
Operation to be executed inside Object Store - Find by Object ID, Find By Query, Insert, Aggregate, Update By Object ID, Update By Query, Delete By Object ID, Delete By Query, Create Index, List Indexes and Drop Index.
Find by Object ID
String
Object Store Name
Name of the collection to be used to record or read information. If it doesn't exist, it will be automatically created.
sales
String
Expire After Seconds (DB)
Defines the number of seconds after which a document from the Object Store expires.
0
Integer
Object ID (DB)
Identifier of the object to be stored or searched. It can be a unique number or a UUID. This item supports Double Braces.
1
String
Limit (DB)
Maximum number of objects to be returned in a search. This item supports Double Braces.
0
Integer
Skip (DB)
Amount of objects to be skipped before returning to the query. This parameter is usually used along with the Limit parameter to create a way of pagination. This item supports Double Braces.
0
Integer
Sort (DB)
Specification of the query ordination rules.
N/A
String
Query (DB)
This JSON field for a query is available only if Find by Query, Aggregate, Update by Query, Delete by Query, Create Index or Drop Index operations are selected.
N/A
String
Document (DB)
Available only if Insert, Update by Object ID, or Update by Query are selected. Double braces expressions are supported.
N/A
String
Unique Index
If the option is activated, an Object ID will be created to accept unique values only; otherwise, a non-unique index will be created.
True
Boolean
Isolated
If the option is activated, all the queries will be delimited in the execution scope.
False
Boolean
Upsert
This option is available only if Update By Object ID or Update By Query operations are selected. When enabled, the item informed for the object will be inserted in the collection in case it doesn't exist.
False
Boolean
Fail On Error
If the option is enabled, the execution of the pipeline with error will be interrupted; otherwise, the pipeline execution proceeds, but the result will show a false value for the “success” property.
False
Boolean
Best practices
Object Store is an auxiliary database (NoSQL) for integrations. Its use provides more agility and practicality in the development of integrations. To exemplify the applicability of this connector, we list the following good usage practices:
The Object Store connector has the function of an intermediary database, i.e., it is used to mediate information between the flows of an integration. It must therefore only be used to store information that is relevant to the integration in question.
The Object Store is a temporary database. Once it’s used to intermediate relevant information for the integration flow, old and dispensable data must be regularly removed from the database. You can remove them manually or create an index with a TTL mechanism to automatically expire the old data.
Since it is an auxiliary base, the Object Store connector must not be used as a permanent database and only in certain cases, with the purpose of supporting the user in the development of integrations.
All data is stored with maximum security within the Digibee Integration Platform. However, we recommend that sensitive data stored in the Object Store be encrypted. To do this, use our encryption connectors available in Canvas.
Messages flow
Input
For this specific connector, the only mandatory input message pattern is the JSON format applied to the object. The input parameter can use the Double Braces syntax to send the received message to the connector.
Output
Insert
Find
Update
Delete
Aggregate
Object Store in action
Some output examples of each operation were shown above. See below more applications that demonstrate the correct configuration for a determined result to be obtained:
Insert multiple items at once in a collection
When sending an object array in the query field, the connector inserts each item in a separate way inside the selected collection.
Observe how to configure the connector with the Operation (Insert), Unique Index (False) and Query parameters:
Output
Find items from a determined query
As an example, consider an Object Store that already has registered product-type items and whose characteristics are name and price.
Observe how to configure the connector with the Operation (Find By Query) and Query parameters:
Output
Find all the items from a query
As an example, consider an Object Store that already has registered product-type items and whose characteristics are name and price.
Observe how to configure the connector with the Operation (Find By Query), Limit (10) and Query parameters:
Output
In this specific scenario, the Limit parameter was configured so there wouldn't be an unnecessary overload when returning the objects from an Object Store. If the option isn't configured that way, an "Out Of Memory" error can occur inside the pipeline. In the indicated way, there's control over how many objects are seen in the response.
Update an item from a specific ID
As an example, consider an Object Store that already has registered product-type items and whose characteristics are name and price.
Observe how to configure the connector with the Operation (Update By Object ID), Object ID (3) and Document parameters:
Output
In this specific scenario, it's possible to see that the output is only an object identifying an update. To check if the object has been properly updated, repeat the ID search scenario.
Remove an item from a specific ID
As an example, consider an Object Store that already has registered product-type items and whose characteristics are name and price.
Observe chow to configure the connector with the Operation (Delete By Object Id) and Object ID (4) parameters:
Output
In this specific scenario, it's possible to see that the output is only an object that identifies the update. To check if the object has been properly updated, repeat the ID search scenario.
Aggregation to copy the collection
As an example, consider an Object Store called "product" that already has registered product-type items and whose characteristics are name and price. From that, create a new Object Store called "product-backup", copying all the items of the collection mentioned above.
You must receive an object array containing the query aggregation pipelines in the Document parameter.
Observe how to configure the connector with the Operation (Aggregate) and Query parameters:
In this specific scenario, the query was configured to replace the repeated items with the new ones in the collection.
Output
To check if the collection has been properly created with the proposed items, repeat the search scenario with all the items and inform the new collection.
Aggregation to filter collection items
You must receive an object array containing the query aggregation pipelines in the Document parameter.
Observe how to configure the connector with the Operation (Aggregate) and Query parameters:
In this specific scenario, the query was configured to search products that has a determined value and to show their sum.
Output
Create an index with expiration time
With the Object Store it’s possible to create an index with a TTL (Time to live) attribute, with which you can define an expiration strategy for the documents. This behavior is controlled in the Expire after seconds parameter. Here are some examples of how you can create indexes with expiration strategies:
Create an index with constant TTL
See an example for the configuration of the parameters Expire after seconds and Query:
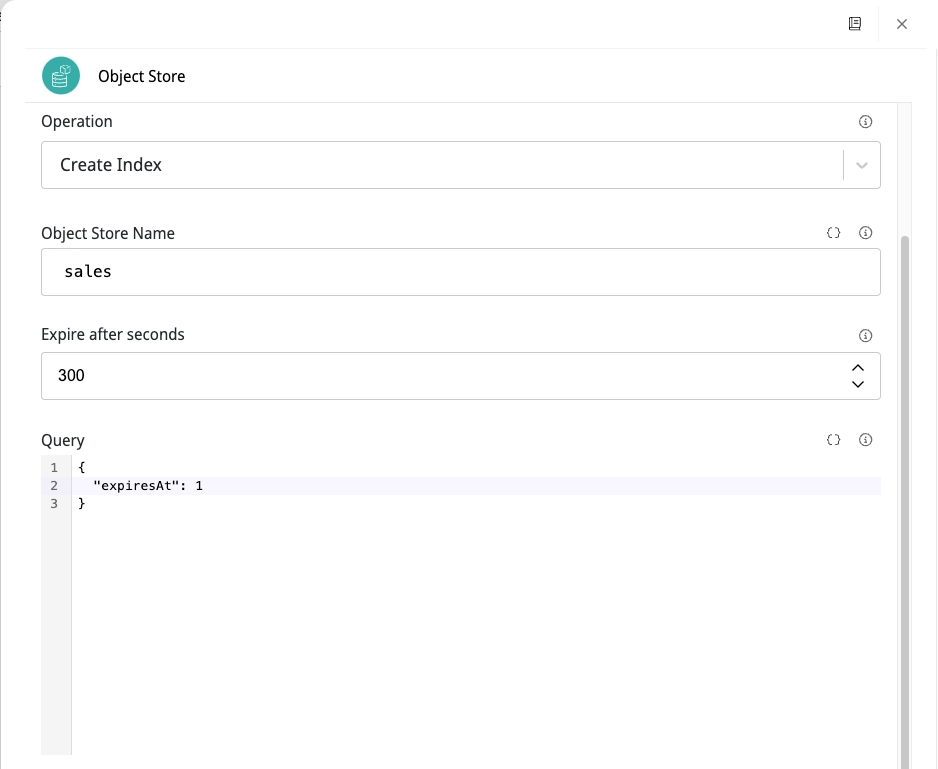
The name of the field must match the date attribute of your document, which will control the lifetime of the object. In addition, all documents with this field are automatically deleted after the number of seconds specified in the Expire after seconds parameter.
Output
Create an index with custom dates
See an example for the configuration of the parameters Expire after seconds and Query:
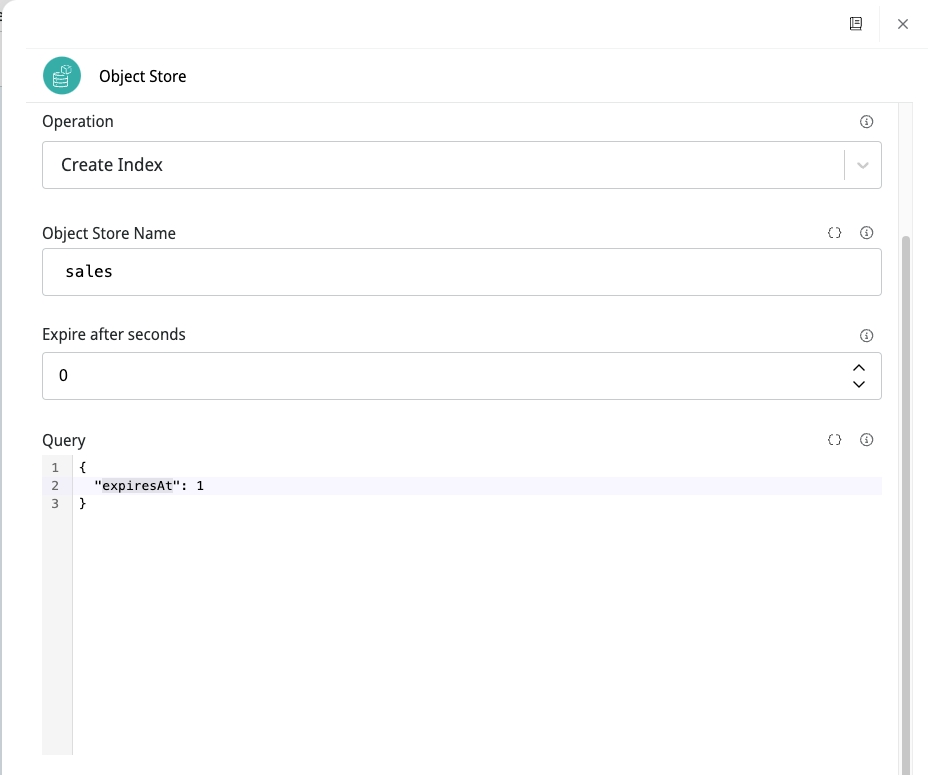
The name of the field must match the date attribute of your document, which will control the lifetime of the object. You must also set the Expire after seconds parameter to 0.
In this scenario, the expiration is defined with the datetime defined in the value of the corresponding field in the Query parameter.
List all indexes
This operation must list all indexes that the user has created in an Object Store.
Output
Drop an existing index
In this operation, it’s possible to drop an index previously created by the customer.
See how to configure the connector with the Drop Index Operation and Query parameter:
Output
Technology
Object Store uses search operators and objects aggregation similar to the MongoDB syntax. Refer to the MongoDB external documentation to learn more.
Last updated
Was this helpful?